Wolves201, CC BY-SA 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
![]()
This article was originally published on The New York Times.
“This year, roughly a quarter of the vast Pantanal wetland in Brazil, one of the most biodiverse places on Earth, has burned in wildfires worsened by climate change. What happens to a rich and unique biome when so much is destroyed?
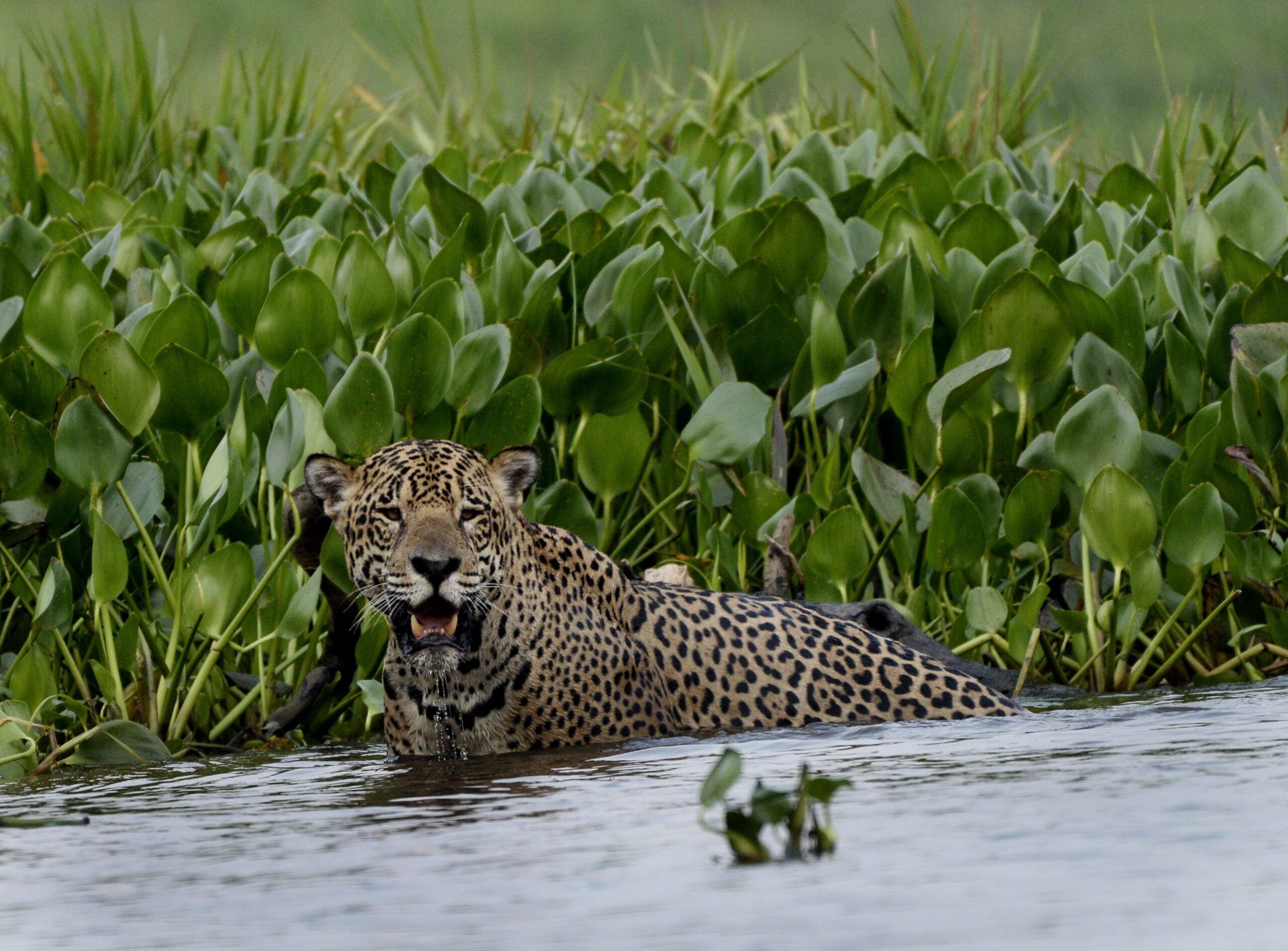
The unprecedented fires in the wetland have attracted less attention than blazes in Australia, the Western United States and the Amazon, its celebrity sibling to the north. But while the Pantanal is not a global household name, tourists in the know flock there because it is home to exceptionally high concentrations of breathtaking wildlife: Jaguars, tapirs, endangered giant otters and bright blue hyacinth macaws. Like a vast tub, the wetland swells with water during the rainy season and empties out during the dry months. Fittingly, this rhythm has a name that evokes a beating heart: the flood pulse.
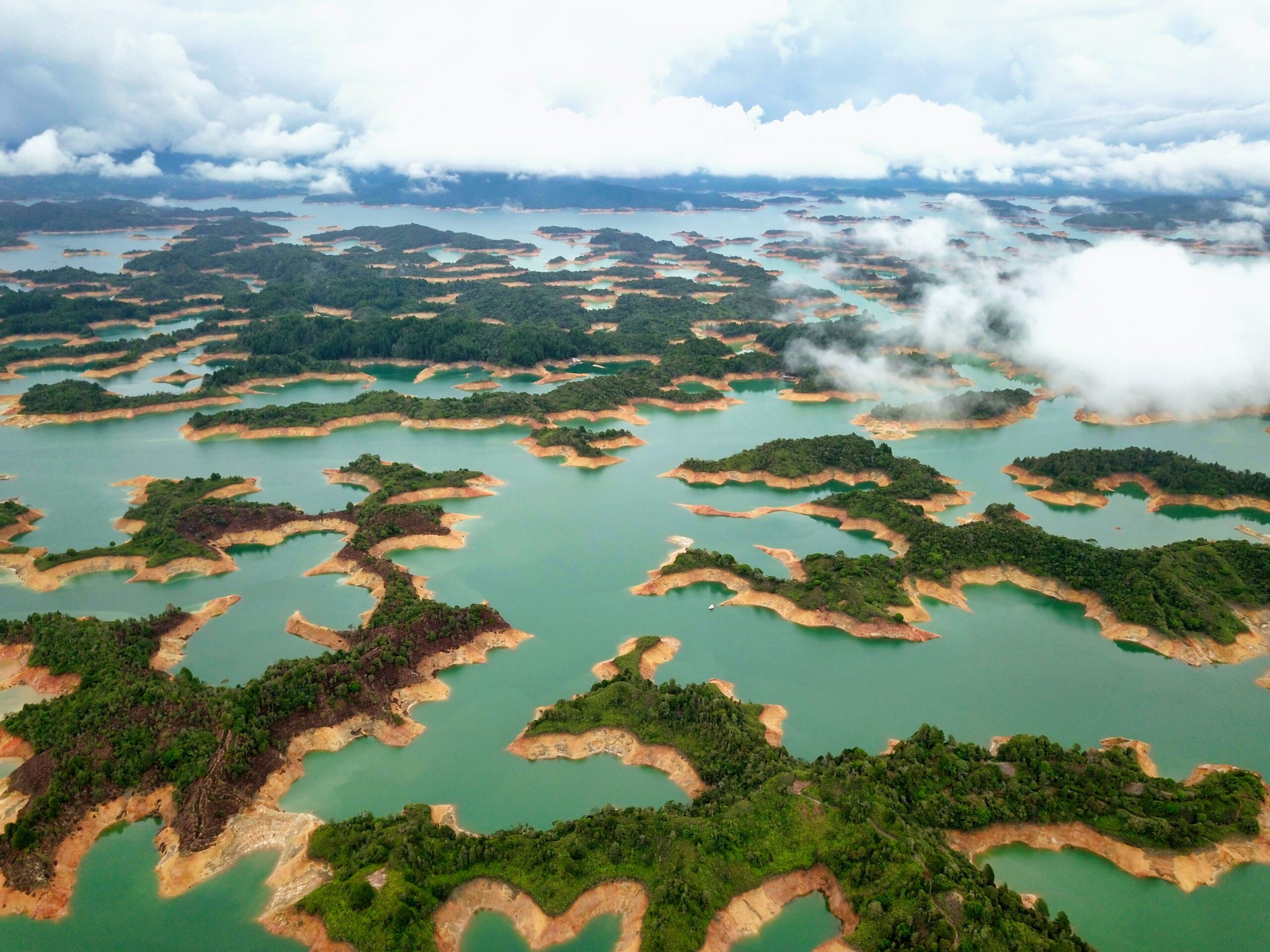
The wetland, which is larger than Greece and stretches over parts of Brazil, Paraguay and Bolivia, also offers unseen gifts to a vast swath of South America by regulating the water cycle upon which life depends. Its countless swamps, lagoons and tributaries purify water and help prevent floods and droughts. They also store untold amounts of carbon, helping to stabilize the climate.
For centuries, ranchers have used fire to clear fields and new land. But this year, drought worsened by climate change turned the wetlands into a tinderbox and the fires raged out of control.
“The extent of fires is staggering,” said Douglas C. Morton, who leads the Biospheric Sciences Laboratory at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and studies fire and food production in South America. “When you wipe out a quarter of a biome, you create all kinds of unprecedented circumstances.”
His analysis showed that at least 22 percent of the Pantanal in Brazil has burned since January, with the worst fires, in August and September, blazing for two months straight.
Naturally occurring fire plays a role in the Pantanal, in addition to the burning by ranchers. The flames are usually contained by the landscape’s mosaic of water. But this year’s drought sucked these natural barriers dry. The fires are far worse than any since satellite records began.”
Read on at: The New York Times